
How AI Enhances Summative Feedback Systems
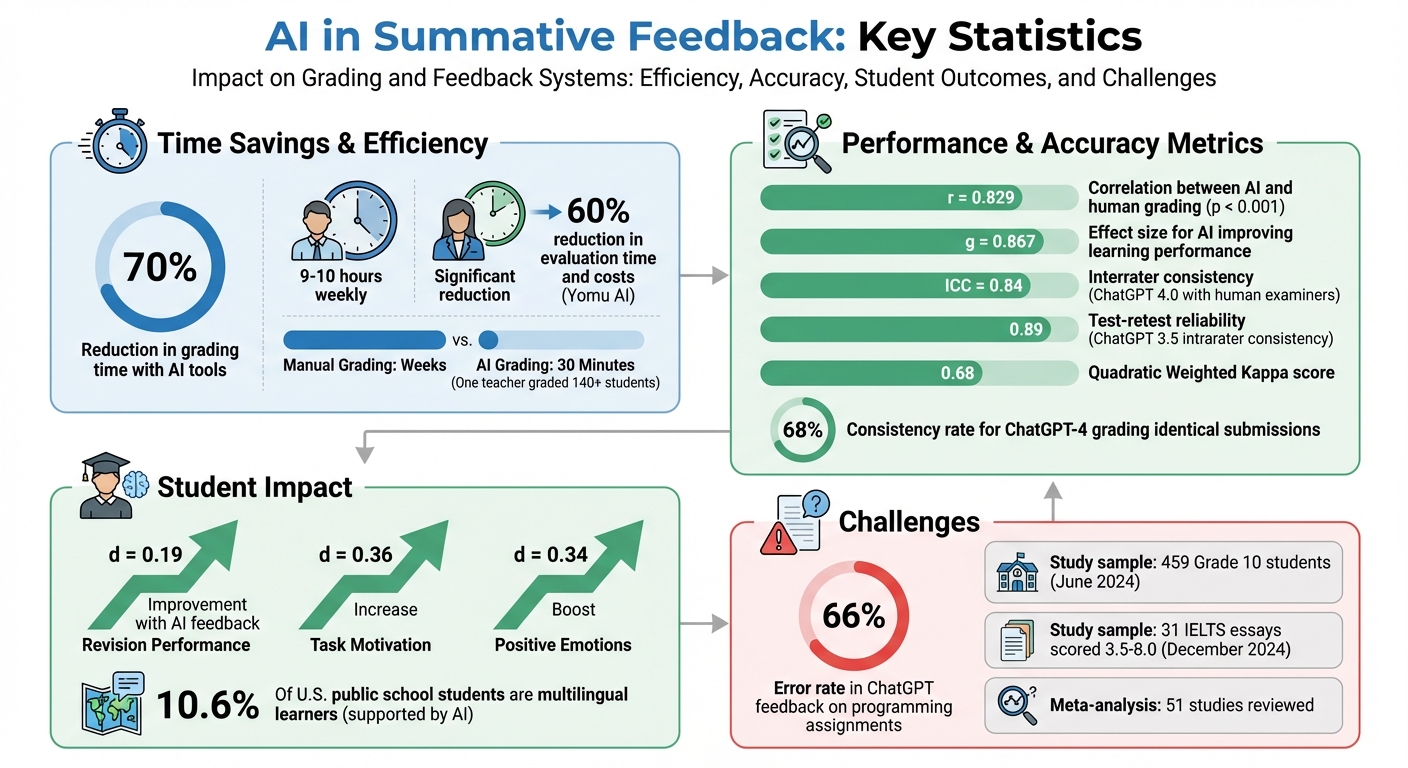
Grading student work takes a lot of time, with educators spending 9–10 hours weekly on it. AI tools are changing this by making grading faster, more consistent, and personalized. Here's how AI is improving summative feedback:
- Faster Grading: AI reduces grading time by up to 70%, handling tasks in hours instead of weeks.
- Personalized Feedback: AI provides detailed, tailored feedback for each student, identifying strengths and areas for improvement.
- Fairer Evaluations: AI uses consistent rubrics, reducing human bias caused by fatigue or personal preferences.
- Advanced Tools: Technologies like NLP and machine learning analyze essays, predict performance, and provide actionable insights.
- Challenges: AI systems need human oversight to ensure accuracy, avoid algorithmic bias, and maintain data privacy.
AI doesn't replace teachers but supports them by saving time and offering tools to improve student learning outcomes. However, effective usage requires careful integration and human review.
AI Impact on Grading: Key Statistics and Performance Metrics
I Let AI Grade My Students. They Liked It Better.
How AI Improves Summative Feedback
AI addresses the key challenges of grading - efficiency, tailored insights, and fairness - by leveraging its strengths in speed, personalized feedback, and objectivity.
Automated Grading for Faster Results
AI-powered grading systems can process assignments much faster than traditional methods. Using natural language processing, they analyze grammar and semantics, while machine learning adapts to rubrics derived from historical grading data. Computer vision even allows these systems to evaluate handwritten submissions. Advanced technologies like CNNs, LSTMs, and BERT-based models work together to assess essays on multiple levels, ensuring consistency and eliminating human bias. These systems apply grading criteria uniformly across all submissions, maintaining fairness and accuracy.
As Springer explains:
AI-driven grading systems also pave the way for real-time feedback, vital for student learning.
This speed doesn’t just improve efficiency - it also opens the door to more personalized, actionable feedback.
Personalized Feedback for Students
AI provides detailed feedback by deeply analyzing each student's work. A randomized controlled study conducted in June 2024 with 459 Grade 10 students showed that feedback generated by GPT-3.5-turbo significantly improved revision performance (d = 0.19) and increased task motivation (d = 0.36) compared to no feedback. AI systems identify individual strengths and weaknesses, helping students address specific learning gaps.
Additionally, AI supports multilingual learners - who make up 10.6% of U.S. public school students - by offering language assistance. This level of personalization, once impossible to achieve at scale, is now within reach.
Reducing Bias in Assessments
AI also brings fairness to the grading process by strictly adhering to predefined rubrics. It eliminates issues like grader fatigue, personal preferences, and unconscious biases that can arise from a student's background. By focusing solely on the content of submissions, AI ensures impartial evaluations. However, to avoid introducing algorithmic bias, developers must train these systems on diverse datasets that reflect the broad range of student populations.
Through its ability to streamline grading, tailor feedback, and uphold fairness, AI is redefining how summative feedback is delivered.
AI Techniques Used in Summative Feedback
AI has revolutionized the way summative feedback is delivered by leveraging techniques like natural language processing (NLP), predictive analytics, and rubric-based scoring. These methods tackle long-standing challenges in traditional grading, offering faster, more precise, and consistent evaluations.
Natural Language Processing for Essay Grading
NLP-powered algorithms dive deep into text analysis, employing advanced models such as CNNs, LSTMs, and transformer-based systems like BERT. These tools excel at identifying context and subtle nuances within essays, uncovering insights that older methods often miss.
A study conducted in December 2024 at Monash University Malaysia evaluated ChatGPT 3.5, ChatGPT 4.0, and Claude 3.0 on 31 official IELTS sample essays, with scores ranging from 3.5 to 8.0. When provided with detailed rubric descriptors, ChatGPT 4.0 demonstrated strong interrater consistency (ICC = 0.84) with human examiners, while ChatGPT 3.5 achieved high test-retest reliability, scoring 0.89 for intrarater consistency. A key takeaway from this research was that domain-specific knowledge often outweighs the complexity of the AI model. As Da-Wei Zhang from Monash University explained:
Our findings indicate that domain-specific knowledge, rather than the complexity or general knowledge/abilities of the LLMs, limits the precision of criterion-based grading.
This capability not only improves grading accuracy but also lays a foundation for predicting students' future performance.
Predictive Analytics for Performance Evaluation
Predictive analytics uses data from test scores, submission patterns, academic records, and even student behaviors to uncover trends that might escape human evaluators. Tools like CoGrader describe this as a "data-driven x-ray of your class's performance". These systems do more than just assess current work - they identify learning gaps and anticipate future challenges, enabling educators to step in before issues escalate.
Meta-analyses of 51 studies highlight the effectiveness of AI in improving learning outcomes, showing an effect size of g = 0.867. This predictive ability transforms summative feedback into a forward-looking resource, helping educators shape future instruction while addressing current needs.
Rubric-Based AI Scoring Systems
Rubric-based systems bring a structured approach to AI grading, ensuring evaluations are consistent across key areas like content quality, organization, writing style, and grammar. The secret to their accuracy lies in detailed, well-defined band descriptors, which help align AI assessments with human grading standards.
One such tool, CoGrader, is used in over 1,000 schools and integrates seamlessly with platforms like Google Classroom and Canvas. This system enables teachers to grade narrative assignments for large groups of students - sometimes 85 or more - in mere seconds, compared to the weeks it would take manually. It also provides actionable "glow and grow" feedback, empowering students to revise their work immediately. As one writing teacher observed:
Students view AI as more objective, and they don't take AI feedback personally. Now, I'm not the one hovering over their writing with my metaphorical red pen; instead, I'm the teacher who can help them improve it.
These rubric-based systems not only save time but also shift classroom dynamics, allowing teachers to focus more on guiding improvement rather than just grading.
How to Add AI to Your Feedback Workflow
Bringing AI into your feedback process requires thoughtful preparation. Start by gathering all necessary grading materials and putting safeguards in place to ensure the technology improves your workflow rather than complicating it. Before diving in, define your objectives, set aside time for adjustments, and establish methods to verify the system's reliability.
Choosing the Right AI Tools
Start with platforms that your institution has already approved, ensuring they comply with FERPA and GDPR standards. Options like Microsoft Copilot, ChatGPT Edu, or Google Gemini are often pre-approved by universities to protect student data. Tools such as Yomu AI can assist with academic writing by refining text and checking originality.
When selecting tools, focus on those that integrate seamlessly with your Learning Management System. For example, platforms like Gradescope and FeedbackFruits work directly with Canvas, enabling you to streamline workflows without constantly juggling between systems. A practical example: in January 2024, a high school writing teacher used the Brisk Teaching Chrome extension to provide "glow and grow" feedback for over 140 students in just 30 minutes by attaching a rubric to the tool.
From here, evaluate how to align these tools with your academic framework.
Connecting AI with Academic Systems
To integrate AI effectively, you'll need a detailed grading rubric, clear instructions, sample work, and well-crafted prompts. Before applying AI grading to all submissions, manually grade 5–7 assignments and compare those results to the AI-generated grades. This step helps identify any discrepancies early on.
Always remove any personally identifiable information from student work before uploading it to an AI platform. The consistency of AI tools can vary; for instance, ChatGPT-4 assigned the same grade to identical data only 68% of the time. Use structured prompts to clearly define the AI's role. At Pennsylvania State University, for example, reviewers using Microsoft Copilot are instructed to start with: "Please take on the role of a university professor" when summarizing student feedback.
These practices help establish a strong foundation for human oversight.
Maintaining Human Oversight
AI should complement - not replace - human judgment. As King's College London highlights, "GenAI is seen as a tool to support, not replace, human activity, judgement and oversight". Treat AI-generated feedback as a draft that requires your review, refinement, and personalization before sharing it with students. This approach ensures accuracy and fairness in evaluations.
Accuracy is especially important. Research on programming assignments found that ChatGPT's feedback contained errors 66% of the time, and even after 15 test runs, it still produced incorrect statements. Always cross-check AI outputs against student work and implement an appeal process for human review. Additionally, starting July 1, 2025, Pennsylvania State University requires any report using AI to include a disclosure footnote specifying the platform and prompts used. This level of transparency fosters trust and accountability in the feedback process.
sbb-itb-1831901
Benefits and Challenges of AI Feedback Systems
The integration of AI into grading workflows brings both opportunities and hurdles that deserve careful consideration.
Benefits of AI Feedback
AI streamlines grading, freeing up educators to focus on what they do best - teaching. Studies show that AI significantly enhances learning performance, with an effect size of g = 0.867. Tools like ChatGPT demonstrate a strong alignment with human assessors, boasting a correlation coefficient of r = 0.829 and impressive Quadratic Weighted Kappa scores of 0.68.
One of the standout advantages is the ability to provide immediate feedback. This allows students to correct their errors while the material is still fresh in their minds. Research highlights that feedback from large language models (LLMs) not only improves revision (d = 0.19) but also boosts motivation (d = 0.36) and fosters positive emotions in students (d = 0.34).
Another major benefit is the consistency and objectivity AI brings to evaluations. By applying uniform criteria, AI minimizes unconscious biases that might stem from a student’s background or identity. This positions teachers as supportive mentors, enabling them to focus on guiding students rather than spending excessive time grading.
Challenges to Address
Despite these advantages, AI feedback systems are far from flawless. One key limitation is their inability to grasp contextual nuances. For example, AI might fail to identify plot inconsistencies in stories, overlook redundancy, or suggest large-scale structural changes like reorganizing or removing paragraphs.
Algorithmic bias is another pressing concern. If the training data lacks diversity, AI systems risk perpetuating inequalities, potentially disadvantaging certain student groups. Data privacy also remains a significant issue. A notable example is the Los Angeles Unified School District’s AI-powered assistant "Ed", which was discontinued after its developer faced financial troubles, raising questions about the security of collected student data.
Additionally, there’s the danger of students becoming overly reliant on AI-generated feedback. When feedback is too prescriptive, students may stop critically engaging with their work, a phenomenon referred to as "metacognitive laziness". Another challenge lies in the opaque nature of many AI systems. These "black box" algorithms make it difficult for educators to understand how specific scores are determined.
As researcher Latifah Hamdan Alghamdi puts it:
AI feedback should enhance, rather than replace, human teaching, and its ongoing application depends on professional growth and strong governance frameworks.
Balancing these challenges with human oversight ensures that AI remains a tool to support - not replace - effective teaching.
Benefits vs. Challenges Comparison
| Aspect | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Delivers instant results for large classes | Lacks nuance; may miss complex organizational issues |
| Consistency | Uniform grading reduces human bias | Algorithmic bias risks if training data is not diverse |
| Personalization | Identifies learning gaps; provides tailored feedback | Can lead to over-reliance if feedback is followed without critical thinking |
| Accuracy | High correlation with human grading (r = 0.829) | Requires human review to catch potential oversights |
| Transparency | Perceived as objective and less emotionally charged | "Black box" algorithms obscure the reasoning behind scores |
| Data Management | Efficiently handles large volumes of data | Privacy concerns arise if providers fail or face security breaches |
Example: Yomu AI in Action
Yomu AI showcases how artificial intelligence can be effectively applied in academic settings, particularly in streamlining grading and feedback processes.
Using Yomu AI for Essay Analysis
Yomu AI offers a suite of tools designed to make essay analysis more efficient. Its paraphrasing and summarization features quickly distill the main arguments of an essay, helping educators assess whether learning objectives are being met. Additionally, its autocomplete function for sentences and paragraphs provides insights into how well students structure their arguments.
The platform also includes a plagiarism checker and a citation tool to ensure academic integrity. The plagiarism checker plays a critical role in verifying originality before final grading, while the citation tool helps educators confirm that sources are properly credited during evaluations.
Streamlining Feedback with Yomu AI
One of Yomu AI's standout features is its ability to pre-screen submissions, flagging both exemplary work and outliers. Studies suggest that tools like Yomu AI can reduce evaluation time and associated costs by up to 60%. Its summarization capabilities allow instructors to identify class-wide trends, enabling them to focus on submissions that require extra attention.
This is particularly helpful when managing a large number of essays. Instead of reading each essay in full during the initial review, educators can rely on AI-generated summaries to spot recurring themes and assess overall performance trends. As Dan Bousfield, Assistant Professor at Western University, explains:
If you're performing the same task repeatedly, it's a candidate for automation using AI tools, coding, or APIs.
Still, it’s important to emphasize that final grading and evaluative decisions should always remain in the hands of human instructors to preserve the educational purpose. These tools not only enhance the feedback process but also pave the way for more efficient integration of AI in academic workflows.
Conclusion
AI is transforming summative feedback by offering quicker, more consistent, and personalized assessments. By combining automated grading with natural language processing, these systems provide tailored guidance to students, addressing some of the long-standing challenges in education. In fact, studies demonstrate a strong correlation (r = 0.829, p < 0.001) between AI-powered tools and human assessors in terms of accuracy and reliability. However, to fully harness this potential, AI must be used alongside informed human judgment.
While AI excels at delivering rapid and customized feedback, its real strength lies in supporting educators rather than replacing them. Tools like Yomu AI streamline time-consuming tasks such as plagiarism detection, citation checks, and essay summarization, allowing teachers to focus on more in-depth evaluations. Research from the University of Michigan in Fall 2024 revealed that teaching assistants using AI-powered feedback tools achieved greater consistency and were able to craft more personalized guiding questions compared to traditional methods. Yet, critical tasks like final grading decisions, evaluative judgments, and addressing complex student challenges must remain firmly in human hands. As Latifah Hamdan Alghamdi from King Khalid University aptly puts it:
AI feedback should enhance, rather than replace, human teaching, and its ongoing application depends on professional growth and strong governance frameworks.
This balanced approach is already making an impact. Tools like Yomu AI, when paired with detailed rubrics and transparent processes, are improving learning outcomes. For instance, AI-enhanced feedback systems have been shown to significantly boost learning performance (g = 0.867), while also increasing student motivation (d = 0.36) and fostering positive emotions (d = 0.34). By blending AI's efficiency with the expertise of educators, we can create feedback systems that are not only scalable but also deeply responsive to the unique needs of students.
FAQs
How does AI promote fairness and minimize bias in grading?
AI helps create a more consistent grading process by using standardized criteria to evaluate all submissions uniformly. This eliminates the influence of subjective factors, like personal preferences or unconscious biases, which can sometimes affect human graders.
That said, fairness also hinges on tackling algorithmic bias. To address this, developers are constantly working on refining AI models, aiming to enhance their transparency and accuracy. These efforts are essential to ensure that AI-driven assessments are as equitable and reliable as possible.
What challenges come with using AI in feedback systems?
Integrating AI into feedback systems comes with its own set of hurdles. One of the biggest concerns is bias - AI algorithms can unintentionally produce feedback that's unfair or inaccurate. This has sparked discussions about the importance of ethical guidelines and transparency in how these systems are designed and used. There's also the issue of data privacy. Since these tools often need access to sensitive student information, questions arise about how securely that data is stored and protected.
Another concern is the potential loss of the personal touch in education. Many educators worry that over-reliance on AI could erode the connection between teachers and students, which is essential for building trust and fostering a positive learning environment.
To tackle these challenges, it's crucial to implement AI thoughtfully. This means setting clear guidelines, ensuring regular oversight, and prioritizing fairness, privacy, and the human element in teacher-student interactions. AI should be a tool that enhances, not replaces, the meaningful relationships at the heart of education.
How can teachers ensure accuracy and fairness when using AI for grading?
Teachers can maintain fairness and precision in grading by using AI tools as a complement to their own expertise rather than a substitute. AI can streamline the process, but it’s essential for educators to review and validate the feedback it generates. Setting up clear guidelines, like routinely checking for potential biases or errors, helps ensure that grading stays consistent with academic standards.
Being transparent with students is equally important. Teachers should explain how AI contributes to evaluations and encourage students to share their thoughts on the process. Additionally, proper training equips educators to critically analyze AI-generated insights, ensuring the technology enhances evaluations while keeping human judgment at the forefront.
